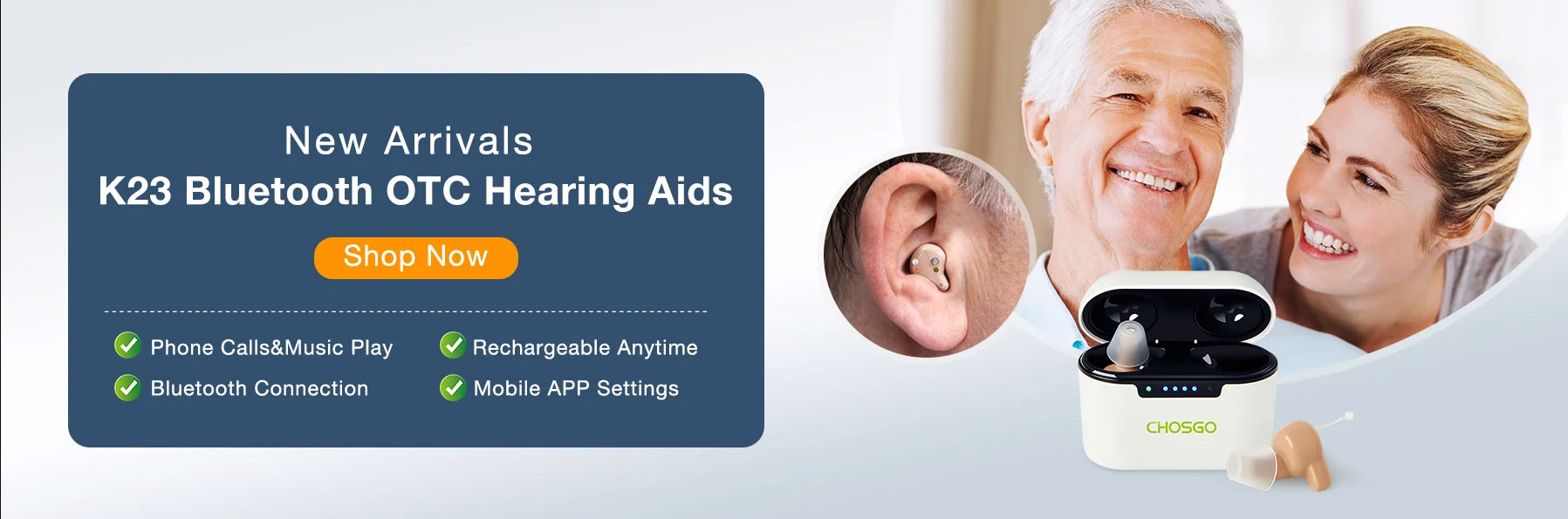
sloping hearing loss
- Date:
- Views:23
ASSISTIVE LISTENING ADVANCES: LEVERAGING MINIATURIZATION FOR ENHANCED AUDIO EXPERIENCE
Throughout background, efforts have been made to improve audio for people experiencing hearing loss, dating back centuries. First efforts included standard devices such as loudspeakers and ear trumpets, which intended to focus and intensify acoustic waves. While these tools gave some help, they were far from ideal. They were commonly cumbersome and bothersome, drawing undesirable focus and offering restricted sound high quality.
The Advent of Digital Hearing Aids: A Considerable Leap Onward
The intro of electronic hearing aids in the very early 20th century represented a substantial development. These tools used vacuum tubes to enhance sound online, providing a substantial improvement over their non-electronic counterparts. Nevertheless, they were still quite bulky and prone to responses, a piercing whistling noise that could be uncomfortable for the user.
Miniaturization and Function Developments: Embracing Smaller Sized Solutions
The renovation of transistors within the mid-20th century led the way for a vital shift in listening device modern technology. Transistors, being significantly smaller and much more efficient than vacuum tubes, made it possible for the intro of smaller sized and added portable hearing aids. This marked the start of an adventure towards miniaturization, leading to a growing number of very discreet and tight tools.
In the second fifty percent of the 20th century, there were developments in miniaturization, such as the growth of integrated circuits (ICs) in the 1970s. ICs, smaller than transistors, allowed size decreases and the addition of additional attributes like multi-band compression and noise reduction. These enhancements improved sound quality, reduced exhaustion while listening, and gave an extra natural and comfy listening experience.
The Digital Change has caused a new level of advancement in listening device. Unlike older analog designs that simply magnified audio, digital listening devices use electronic signal processing (DSP) to convert inbound sound waves right into digital signals. These signals can after that be changed and processed to enhance quality, lessen history noise, and get rid of responses.
Digital listening devices offer a wide range of remarkable abilities, along with:
Directional microphones: These microphones understand audios coming from the front, lowering heritage sound and boosting speech intelligibility in loud atmospheres.
AVC (Automatic Quantity Control) is a function that intelligently changes the quantity of your listening devices based upon the ambient sound degree, making certain a comfy paying attention experience in various atmospheres.
Feedback cancellation: This technology appropriately eliminates the irritating whistling sound that might happen in hearing aids.
Customers have the ability to adjust setups to produce special paying attention quiet environments, loud locations music playback.
The Age of Unnoticeable Hearing: Innovations in Mini Innovation
The unrelenting pursuit of advancement in listening devices technology has brought about an innovative era of totally inconspicuous gadgets. These minuscule wonders, consisting of completely-in-canal (CIC) and invisible-in-canal (IIC) versions, are quietly positioned deep within the ear canal, giving an exceptional level of personal privacy and convenience. Furthermore, some hearing aids now flaunt Bluetooth connectivity, allowing seamless audio streaming from smartphones, tablets, and other devices.
The Future of Hearing Aid Technology: Looking Ahead
The destiny of listening to useful resource era holds immense promise. Researchers are always exploring new improvements, which include:
Artificial intelligence (AI): AI-powered listening aids are being developed to customize listening experiences and routinely alter settings primarily based on character desires and possibilities.
The advancement of materials that are compatible with the human body should lead to the development of hearing aids that can be implanted in the middle ear and provide a more natural and discreet hearing experience.
Direct neural stimulation: This era, nonetheless in its early levels, ambitions to stimulate the auditory nerve without delay, bypassing the broken elements of the internal ear and doubtlessly presenting a brand new method of listening to restoration.
Challenges of Miniaturization:
Battery Life: Smaller gadgets often necessitate smaller batteries, leading to shorter lifespans. This may be inconvenient and require frequent battery replacements.
Smaller parts are at a higher risk of damage from moisture, dust, and regular use, which can affect their durability.
It can be challenging to find the right balance between making a device smaller and including all the desired features. Users may have to decide between a compact size and specific functions.
Mobility: For individuals with limited dexterity, particularly older adults, maneuvering and fine-tuning small hearing aids can be problematic.
Considerations for Users:
Individual Needs: Hearing loss varies drastically from character to character. Choosing the proper hearing aid length needs to be balanced with the person listening to wishes and options.
People leading active lifestyles or regularly exposed to tough conditions may value durability more than size.
Accessibility can be a challenge for some customers due to the higher cost of smaller, more advanced hearing aids.
Enhancing Inclusivity: Tackling Stigma and Accessibility in Hearing Loss
While the reduction of size is a significant factor in improving user experience, it is crucial to acknowledge and address the broader concerns related to hearing impairment and accessibility.
Overcoming the Stigma: Despite progress made in addressing hearing loss, a lingering stigma can still hinder individuals from seeking assistance. To overcome this hurdle, education and awareness campaigns can be instrumental in normalizing hearing loss and encouraging individuals to take proactive steps in addressing their hearing needs.
Accessibility and Affordability: Cost stays a prime hurdle for many, limiting get entry to advanced listening aids. Expanding coverage and exploring cheap hearing aid options are essential to ensuring inclusivity.
Expanding access to hearing healthcare through telehealth and remote care services can significantly benefit individuals in underserved communities.
In conclusion, by emphasizing the significance of small-scale solutions and the importance of human connection, we can shape a future where individuals with hearing loss can fully engage with their surroundings, contribute positively to society, and enjoy the joy of clear and meaningful conversations. Achieving this vision requires a comprehensive approach that combines technological advancements with empathy, training, and societal support. Only then can we guarantee that everyone has the opportunity to flourish in a world filled with sound.
Best OTC Hearing Aids hearing aids near me hearing aids online hearing test hearing aids
Throughout background, efforts have been made to improve audio for people experiencing hearing loss, dating back centuries. First efforts included standard devices such as loudspeakers and ear trumpets, which intended to focus and intensify acoustic waves. While these tools gave some help, they were far from ideal. They were commonly cumbersome and bothersome, drawing undesirable focus and offering restricted sound high quality.
The Advent of Digital Hearing Aids: A Considerable Leap Onward
The intro of electronic hearing aids in the very early 20th century represented a substantial development. These tools used vacuum tubes to enhance sound online, providing a substantial improvement over their non-electronic counterparts. Nevertheless, they were still quite bulky and prone to responses, a piercing whistling noise that could be uncomfortable for the user.
Miniaturization and Function Developments: Embracing Smaller Sized Solutions
The renovation of transistors within the mid-20th century led the way for a vital shift in listening device modern technology. Transistors, being significantly smaller and much more efficient than vacuum tubes, made it possible for the intro of smaller sized and added portable hearing aids. This marked the start of an adventure towards miniaturization, leading to a growing number of very discreet and tight tools.
In the second fifty percent of the 20th century, there were developments in miniaturization, such as the growth of integrated circuits (ICs) in the 1970s. ICs, smaller than transistors, allowed size decreases and the addition of additional attributes like multi-band compression and noise reduction. These enhancements improved sound quality, reduced exhaustion while listening, and gave an extra natural and comfy listening experience.
The Digital Change has caused a new level of advancement in listening device. Unlike older analog designs that simply magnified audio, digital listening devices use electronic signal processing (DSP) to convert inbound sound waves right into digital signals. These signals can after that be changed and processed to enhance quality, lessen history noise, and get rid of responses.
Digital listening devices offer a wide range of remarkable abilities, along with:
Directional microphones: These microphones understand audios coming from the front, lowering heritage sound and boosting speech intelligibility in loud atmospheres.
AVC (Automatic Quantity Control) is a function that intelligently changes the quantity of your listening devices based upon the ambient sound degree, making certain a comfy paying attention experience in various atmospheres.
Feedback cancellation: This technology appropriately eliminates the irritating whistling sound that might happen in hearing aids.
Customers have the ability to adjust setups to produce special paying attention quiet environments, loud locations music playback.
The Age of Unnoticeable Hearing: Innovations in Mini Innovation
The unrelenting pursuit of advancement in listening devices technology has brought about an innovative era of totally inconspicuous gadgets. These minuscule wonders, consisting of completely-in-canal (CIC) and invisible-in-canal (IIC) versions, are quietly positioned deep within the ear canal, giving an exceptional level of personal privacy and convenience. Furthermore, some hearing aids now flaunt Bluetooth connectivity, allowing seamless audio streaming from smartphones, tablets, and other devices.
The Future of Hearing Aid Technology: Looking Ahead
The destiny of listening to useful resource era holds immense promise. Researchers are always exploring new improvements, which include:
Artificial intelligence (AI): AI-powered listening aids are being developed to customize listening experiences and routinely alter settings primarily based on character desires and possibilities.
The advancement of materials that are compatible with the human body should lead to the development of hearing aids that can be implanted in the middle ear and provide a more natural and discreet hearing experience.
Direct neural stimulation: This era, nonetheless in its early levels, ambitions to stimulate the auditory nerve without delay, bypassing the broken elements of the internal ear and doubtlessly presenting a brand new method of listening to restoration.
Challenges of Miniaturization:
Battery Life: Smaller gadgets often necessitate smaller batteries, leading to shorter lifespans. This may be inconvenient and require frequent battery replacements.
Smaller parts are at a higher risk of damage from moisture, dust, and regular use, which can affect their durability.
It can be challenging to find the right balance between making a device smaller and including all the desired features. Users may have to decide between a compact size and specific functions.
Mobility: For individuals with limited dexterity, particularly older adults, maneuvering and fine-tuning small hearing aids can be problematic.
Considerations for Users:
Individual Needs: Hearing loss varies drastically from character to character. Choosing the proper hearing aid length needs to be balanced with the person listening to wishes and options.
People leading active lifestyles or regularly exposed to tough conditions may value durability more than size.
Accessibility can be a challenge for some customers due to the higher cost of smaller, more advanced hearing aids.
Enhancing Inclusivity: Tackling Stigma and Accessibility in Hearing Loss
While the reduction of size is a significant factor in improving user experience, it is crucial to acknowledge and address the broader concerns related to hearing impairment and accessibility.
Overcoming the Stigma: Despite progress made in addressing hearing loss, a lingering stigma can still hinder individuals from seeking assistance. To overcome this hurdle, education and awareness campaigns can be instrumental in normalizing hearing loss and encouraging individuals to take proactive steps in addressing their hearing needs.
Accessibility and Affordability: Cost stays a prime hurdle for many, limiting get entry to advanced listening aids. Expanding coverage and exploring cheap hearing aid options are essential to ensuring inclusivity.
Expanding access to hearing healthcare through telehealth and remote care services can significantly benefit individuals in underserved communities.
In conclusion, by emphasizing the significance of small-scale solutions and the importance of human connection, we can shape a future where individuals with hearing loss can fully engage with their surroundings, contribute positively to society, and enjoy the joy of clear and meaningful conversations. Achieving this vision requires a comprehensive approach that combines technological advancements with empathy, training, and societal support. Only then can we guarantee that everyone has the opportunity to flourish in a world filled with sound.
Best OTC Hearing Aids hearing aids near me hearing aids online hearing test hearing aids